2024: Data Breach Costs Rise & AI’s Cybersecurity Impact

The 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report by IBM and Ponemon Institute paints a stark picture of the evolving cybersecurity landscape. While AI is emerging as a potent tool for cost savings, the overall cost of data breaches continues to rise. Overall, the 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report provides valuable insights for organizations navigating the complex cybersecurity landscape. Embracing AI, addressing the skills gap, and proactively managing data are key steps towards reducing breach costs and mitigating risks. Let’s dive into what’s on our plate in 2024!
Data Breach Costs Soar to Record Highs
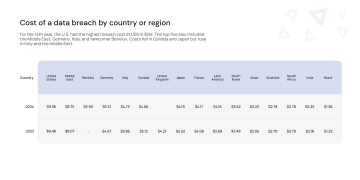
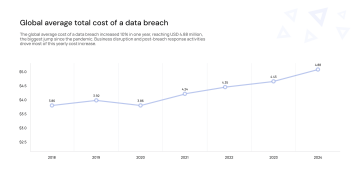
The average cost of data breaches has been on a steady upward trajectory, reaching a record high of USD 4.88 million in 2023. This represents a significant increase of 10% from the previous year's average cost of USD 4.45 million, and it is the most significant increase observed since the onset of the pandemic. Several factors have contributed to this alarming rise.
One major factor driving the increase in data breach costs is the growing financial impact of lost business. Operational downtime and customer attrition play significant roles in this regard. When a data breach occurs, businesses often experience disruptions to their operations, leading to lost productivity, reputational damage, and a decline in customer trust. These disruptions can result in substantial financial losses, as customers may choose to take their business elsewhere.
Another factor contributing to the increase in data breach costs is the rising cost of post-breach response activities. These activities include staffing customer service help desks to address inquiries and concerns from affected individuals, as well as paying higher regulatory fines imposed by government agencies for non-compliance with data protection regulations. These costs can add up quickly, further exacerbating the financial burden of data breaches.
The combined cost of lost business and post-breach activities reached a staggering USD 2.8 million in 2023, the highest combined amount recorded over the past six years. This figure highlights the significant financial implications of data breaches, emphasizing the need for organizations to prioritize cybersecurity measures and invest in robust data protection strategies.
Significant Cost Savings with Extensive AI Adoption
The extensive use of artificial intelligence (AI) in prevention has led to significant cost savings for organizations. According to a recent study, 2 out of 3 organizations surveyed are deploying security AI and automation across their security operations center (SOC), representing a 10% increase from the previous year.
When AI is deployed extensively across prevention workflows, including attack surface management (ASM), red teaming, and posture management, organizations can expect to save an average of USD 2.2 million less in breach costs compared to those with no AI use in prevention workflows. This finding was the largest cost savings revealed in the 2024 report.
The benefits of using AI in prevention are numerous. AI can help organizations to:
Identify and prioritize vulnerabilities: AI can scan large amounts of data to identify potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. This allows organizations to focus their resources on addressing the most critical vulnerabilities first.
Detect and respond to attacks: AI can monitor networks for suspicious activity and can automatically respond to attacks. This can help organizations to prevent or mitigate the impact of breaches.
Improve threat intelligence: AI can collect and analyze threat intelligence from a variety of sources to help organizations understand the latest threats and trends. This information can be used to improve security policies and procedures.
In addition to cost savings, AI can also help organizations to improve their security posture and reduce their risk of being breached. By automating many of the tasks involved in security operations, AI can free up security analysts to focus on more strategic tasks. AI can also help organizations to make better decisions about how to allocate their security resources.
Overall, the extensive use of AI in prevention can lead to significant cost savings, improved security posture, and reduced risk of being breached. Organizations that are not already using AI in prevention should consider doing so to reap these benefits.
Cybersecurity Skills Gap Continues to Widen
The cyber skills shortage has become a pressing issue in today's increasingly digital world, affecting organizations across various industries. More than half of organizations that have experienced data breaches are grappling with severe security staffing shortages, a significant increase compared to the previous year. This situation has resulted in an average of USD 1.76 million more in breach costs for affected organizations.
Despite the emergence of generative AI (gen AI) security tools, which are designed to enhance productivity and efficiency, the skills gap remains a significant challenge. While 1 in 5 organizations report using some form of gen AI security tools, the shortage of skilled professionals capable of effectively deploying and managing these tools persists. This situation underscores the need for comprehensive strategies to address the cyber skills gap and mitigate the associated risks.
The factors contributing to the cyber skills shortage are multifaceted. Rapid technological advancements and the growing sophistication of cyber threats have outpaced the development of qualified professionals in the field. The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, requiring professionals to stay abreast of the latest tools, techniques, and best practices. Additionally, the high demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals has created a competitive job market, making it challenging for organizations to attract and retain top talent.
The recent World Economic Forum Whitepaper revealed a remarkable growth of 12.6% in the global cybersecurity workforce from 2022 to 2023, marking a substantial year-over-year increase in the industry. Despite this growth, the white paper emphasizes a significant talent gap, highlighting the urgent need for approximately four million skilled workers in the cybersecurity industry worldwide.
To address the cyber skills shortage, a concerted effort is required from various stakeholders, including educational institutions, industry professionals, and government agencies. Educational institutions need to develop specialized programs that provide students with the necessary skills and knowledge to succeed in cybersecurity careers. Industry professionals should engage in mentorship and training initiatives to nurture the next generation of cybersecurity experts. Government agencies can play a crucial role by providing funding for research and development, as well as implementing policies that promote the development of a skilled cybersecurity workforce.
Shadow Data: The Hidden Risk Amplifying Breach Costs
The proliferation of data, particularly shadow data, poses significant challenges to organizations in terms of data tracking, safeguarding, and breach response. In a recent study, it was found that a substantial 35% of data breaches involved shadow data. This highlights the prevalence of shadow data and the need for organizations to address its risks effectively.
Shadow data theft, a serious concern associated with shadow data, was identified as a factor contributing to a 16% higher cost of a data breach. This finding underscores the financial impact of shadow data breaches, emphasizing the importance of proactive measures to prevent and mitigate such incidents.
Researchers also discovered that storing data across multiple environments, such as public cloud, on-premises, and private cloud, proved to be a common storage strategy. However, this practice was associated with a higher risk of data breaches, accounting for 40% of all breaches. Furthermore, these breaches took longer to identify and contain compared to breaches involving data stored in a single type of environment.
In contrast, data stored in just one type of environment, whether public cloud (25%), on-premises (20%), or private cloud (15%), experienced lower breach rates. This suggests that organizations should carefully consider their data storage strategies and minimize the number of environments in which data is stored to reduce the risk of data breaches.
The study's findings underscore the importance of effective data governance practices to prevent the proliferation of shadow data, implement robust data security measures, and regularly monitor and audit data access and storage. By proactively addressing the risks associated with shadow data, organizations can enhance their data security posture and mitigate the potential financial and reputational damage caused by data breaches.
Customer Data and Intellectual Property: Prime Targets for Breaches
The research revealed a concerning trend in data breaches involving customer personal information (PII) and intellectual property (IP) records. Nearly half (49%) of all breaches analyzed involved the compromise of sensitive PII, including tax identification numbers, email addresses, phone numbers, and home addresses. This highlights the significant risk posed to individuals and organizations alike when this type of information falls into the wrong hands.
In terms of the cost associated with data breaches, the study found a significant increase in the cost of IP records. The average cost per IP record jumped from USD 156 in the previous year's report to USD 173 in the current study, representing a substantial increase. This suggests that organizations need to prioritize the protection of their IP assets, as breaches involving these records can result in significant financial losses.
The findings of the research underscore the urgent need for businesses to strengthen their cybersecurity measures and implement robust data protection practices. Organizations should focus on implementing robust access controls, encrypting sensitive data, regularly updating software and systems, and conducting regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. Failure to do so could result in costly data breaches, reputational damage, and legal consequences.
Additionally, individuals should exercise caution when sharing their personal information online and be wary of phishing scams and other malicious activities. Using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and being vigilant about suspicious emails and websites can help protect against data breaches and identity theft.
Stolen Credentials: A Major Cybersecurity Vulnerability
Breaches involving stolen or compromised credentials pose a significant challenge to organizations, as they often take the longest to identify and contain compared to other attack vectors. On average, it takes 292 days for organizations to detect and mitigate breaches involving stolen credentials, making them among the most time-consuming and difficult incidents to resolve.
Phishing attacks, which involve sending fraudulent emails or messages to trick users into revealing sensitive information or clicking on malicious links, also pose a substantial threat. These attacks often target employees and take advantage of their access to sensitive systems and data. On average, phishing attacks remain active within an organization for approximately 261 days, making them one of the longest-lasting attack vectors.
Similarly, social engineering attacks, which involve manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information or taking specific actions, also take a considerable amount of time to resolve. These attacks typically target employees and exploit their trust and willingness to help others. On average, social engineering attacks persist within an organization for 257 days, making them another persistent and challenging attack vector to address.
Organizations must prioritize implementing robust security measures to protect against these types of attacks. This includes educating employees about the risks of stolen credentials, phishing, and social engineering, as well as implementing strong authentication mechanisms and regularly monitoring for suspicious activities.
Malicious Insider Attacks: The Costliest Threat
In comparison to other attack vectors, malicious insider attacks resulted in the highest costs, averaging USD 4.99 million. This staggering figure highlights the significant impact of insider threats, which can result in severe financial losses for organizations.
Among the other costly attack vectors identified were business email compromise, phishing, social engineering, and stolen or compromised credentials. These vectors often involve exploiting human vulnerabilities or weaknesses in security protocols to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information or systems.
The emergence of generative artificial intelligence (Gen AI) has added a new dimension to these attack vectors, particularly phishing. Gen AI allows even non-native English speakers to easily create grammatically correct and plausible phishing messages, making it increasingly challenging for users to identify malicious emails.
For instance, Gen AI can generate convincing subject lines, body text, and even attachments that appear legitimate but are designed to trick recipients into revealing personal or financial information. This poses a significant challenge for organizations as it increases the likelihood of successful phishing attacks and subsequent data breaches.
To mitigate the risks associated with malicious insider attacks and other sophisticated attack vectors, organizations need to adopt a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that includes:
Heightened Security Awareness: Educating employees about the latest threats, such as malicious insider attacks and phishing scams, and promoting vigilance in identifying suspicious activities.
Robust Access Control: Implementing strict access controls to restrict employee access to sensitive information based on their job roles and responsibilities.
Continuous Monitoring: Utilizing security tools and technologies to continuously monitor network traffic, user behavior, and system activities for any anomalies or suspicious patterns.
Threat Intelligence Sharing: Collaborating with industry peers and security experts to share threat intelligence and best practices for defending against emerging threats.
Incident Response Preparedness: Developing a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a security breach, including containment, eradication, and recovery.
By implementing these measures and staying vigilant against evolving threats, organizations can better protect themselves from the costly consequences of malicious insider attacks and other sophisticated attack vectors.
Law Enforcement: An Effective Tool in Mitigating Ransomware Costs
Ransomware attacks have become increasingly prevalent in recent years, with cybercriminals targeting businesses and organizations of all sizes. While ransomware can be a devastating event, resulting in significant financial losses and operational disruptions, there is evidence that involving law enforcement can help reduce the cost of the breach and shorten the time required to identify and contain it.
According to a recent study by Coveware, a leading ransomware recovery firm, ransomware victims that involved law enforcement ended up lowering the cost of the breach by an average of nearly USD 1 million. This excludes the cost of any ransom paid, which can often amount to hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars.
The study also found that involving law enforcement helped shorten the time required to identify and contain breaches from 297 days to 281 days. This is a significant improvement, as it can help organizations minimize the impact of the attack and get their operations back up and running more quickly.
There are several reasons why involving law enforcement can be beneficial in the event of a ransomware attack. First, law enforcement agencies have the resources and expertise to track down cybercriminals and recover stolen data. They can also work with other law enforcement agencies around the world to coordinate investigations and share intelligence.
Second, involving law enforcement can help deter future attacks. When cybercriminals know that they are likely to be caught and prosecuted, they are less likely to target organizations. Third, law enforcement can provide support and guidance to victims of ransomware attacks. They can help organizations develop a response plan, negotiate with cybercriminals, and recover their data.
Of course, involving law enforcement is not always the right decision. In some cases, it may be more important to focus on recovering data and minimizing disruption to operations. However, for organizations that are able to involve law enforcement, it can be a valuable resource in the fight against ransomware.
Here are some tips for involving law enforcement in a ransomware attack:
Contact your local law enforcement agency as soon as possible.
Provide law enforcement with as much information as possible about the attack, including the date and time of the attack, the amount of ransom demanded, and the type of ransomware used.
Cooperate with law enforcement throughout the investigation.
Be patient, as investigations can take time.
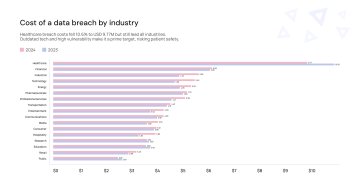
Industrial Sector: Bearing the Brunt of Rising Breach Costs
The industrial sector bore the brunt of the costliest increase in data breach expenses, with an average surge of USD 830,000 per breach year-over-year. This dramatic spike highlights the urgent need for industrial organizations to prioritize rapid response preparedness. The sensitivity of operations in this sector means downtime can have severe consequences. However, the industrial sector's performance in identifying and containing data breaches fell short of the median industry benchmark. It took an average of 199 days to identify and 73 days to contain a breach, underscoring the challenges faced by organizations in this sector in effectively managing cybersecurity risks.
Several factors contribute to the high cost of data breaches in the industrial sector. Firstly, industrial organizations often have complex operational technology (OT) environments, which can make it challenging to implement effective cybersecurity measures. Additionally, the interconnectedness of industrial systems and the reliance on legacy infrastructure can provide numerous entry points for attackers. Furthermore, the highly sensitive nature of industrial data, such as intellectual property and production processes, makes it a valuable target for cybercriminals.
To address these challenges, industrial organizations need to adopt a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity. This includes implementing robust security controls, regularly patching software vulnerabilities, and conducting thorough risk assessments. They also need to invest in security awareness training for employees and contractors and establish incident response plans to minimize the impact of a data breach if it occurs.
By taking these steps, industrial organizations can better protect themselves from the growing threat of cyberattacks and reduce the financial impact of data breaches.
Conclusion
The 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report serves as a stark reminder of the escalating financial repercussions of data breaches. While AI emerges as a beacon of hope, offering significant cost-saving potential, organizations must grapple with a widening cybersecurity skills gap and the growing challenges of securing data in an increasingly complex landscape. The report underscores the critical need for proactive measures, including robust AI-driven security strategies, talent development initiatives, and a relentless focus on protecting sensitive data. By prioritizing these actions, organizations can better position themselves to navigate the ever-evolving threat landscape and safeguard their valuable assets.